AIM

Work Assistance System for the Individualisation of Work Design and Method Training (AIM)
Use of Smart Devices for Context-sensitive Work Support as a New Component of Workplace Health Management
(Project duration: June 2016 to May 2019)
Problem
The increasing dynamics and digitalisation of the world of work in combination with current megatrends, such as short product life cycles, volatile customer requirements and increasing product diversity, result in work processes with a high level of complexity and a low repetition rate. To ensure responsiveness and competitiveness, the use of human labour remains of central importance for manufacturing companies and is also indispensable in the context of a technology-driven Industry 4.0. This leads to ambivalent demands on the employee.
While on the one hand they will increasingly act as conductors and controllers, on the other hand a considerable part of their range of activities will continue to consist of manual, repetitive and sometimes monotonous tasks that can lead to high stress levels. An important feature of these activities is the increased variability of work content and conditions due to work organisation measures (e.g. job rotation, job enrichment). In this context, the current demographic development and the associated inter- and intra-individual dispersion of sensory, motor and cognitive employee abilities have a reinforcing effect.
Objective
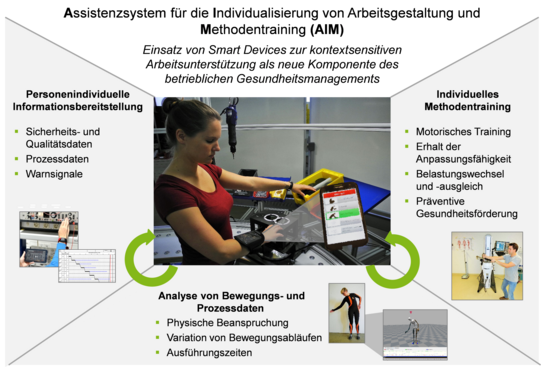
The aim of the research project is to develop a new component of occupational health management (OHM) for the long-term preservation of the adaptability and employability of employees. The targeted sensory, cognitive employee support through a work assistance system at an already designed workplace is of essential importance here. The central aspect of the new component of occupational health management is the linking of ergonomic and structural work design with competence and personnel development.
The employee is supported through the use of smart devices as well as through the development of an innovative training concept taking into account individual requirement profiles and operational framework conditions. With the help of the assistance system, both general (e.g. safety instructions) and specific information (e.g. work tasks, procedures) is provided to the employee individually in a context-sensitive manner, which contributes to an increase in human perception and individual situational awareness and at the same time facilitates decision-making in highly varying work situations. In addition, work assistance is used to record and process relevant movement and process parameters to create the individual training concept. The training, which is used both to learn ergonomically favourable movements and for targeted load change and compensation, also enables situation-dependent visualisation in the workplace by drawing on 3D simulations including digital human models.
Procedure and Division of Labour
The development of the project content is divided into five work packages (analysis and requirements specification, concept, implementation and realisation, validation and optimisation, project management and public relations). First, the relevant basics for the development of the work assistance for the individualisation of work design and method training are worked out and compiled in a catalogue of requirements. Based on this, the comprehensive conception of the work assistance takes place before the developed detailed concepts are to be technically implemented and realised in the form of an individual work assistance. The digital safeguarding of ergonomic work design using a simulation environment is of essential importance here. Finally, the concepts developed must be validated and optimised in representative use cases. The basis for this is the organisational and structural working conditions developed in the context of new forms of industrial work and the resulting physical and mental stresses.
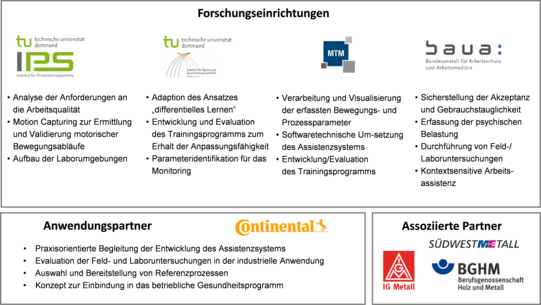
Research- and Development Partner
A particular strength of the interdisciplinary project is the involvement of the Industrial Union of Metalworkers (IG-Metall), the Employers' Association of the Metalworking and Electrical Industry of Baden-Württemberg e.V. (SWM) and the Employers' Liability Insurance Association for Wood and Metal (BGHM).
Förderhinweis
This project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research as part of the programme "Working - Learning - Developing Skills, Preventive Measures for the Safe and Healthy Work of Tomorrow" (funding code 02L14A160) and is supervised by the project management organisation PTKA.

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/storages/zentraler_bilderpool/_processed_/2/6/csm_Altes_Maschinenbau-Gebaeude_3a1a87015a.jpg)


