InDaS
Industrial Data Science (InDaS) - Qualification Concept for Machine Learning in Industrial Production
Problem
The spread of modern information and communication technologies in the context of Industry 4.0 as well as the technological ability to systematically and comprehensively collect and store data make it possible to build dynamic information stores of previously unknown size and quality. The interpretation and efficient use of the knowledge implicitly available in these data stores for decision-making and planning support is increasingly becoming the focus of manufacturing companies. Machine learning methods provide a selection of approaches for the intelligent and automated evaluation of large amounts of data. These enable previously unknown correlations to be identified and visualised, as well as existing a priori knowledge to be checked and used for early forecasting. The knowledge gained in this way, in combination with the practical experience of employees, will be an essential success factor for companies in the future.
Against this background, the company-specific application and use of data analysis methods is receiving increasing attention. Focal points in the industrial use of machine learning methods include use cases such as product family formation and production segmentation, the process-accompanying prognosis of product quality as well as problems in the area of predictive maintenance. Successful and efficient processing of these use cases requires both methodological know-how in the field of statistics and computer science and, due to the often technical nature of the use cases, sound domain knowledge in engineering. However, companies often lack sufficient expertise to meet these challenges. Qualified personnel who are both proficient in the use of machine learning methods and are familiar with the special requirements of companies as well as have sufficient domain knowledge to understand and successfully solve engineering use cases are rarely available.
In the education of young academics as well as in the further training of specialists, this problem is rarely or insufficiently given attention. Training in the field of machine learning is usually subject-specific and thus focuses predominantly on teaching the theoretical content of machine learning, but does not take into account the practical feasibility and the special framework conditions of industrial practice.
Objective and Approach
The aim of the planned research project is therefore to develop an innovative teaching concept for the qualification of young academics and specialists from industry in the field of machine learning. In particular, the special challenges of manufacturing companies are to be taken into account and the participants are thus to be taught the necessary competences for solving machine learning problems in industrial practice.
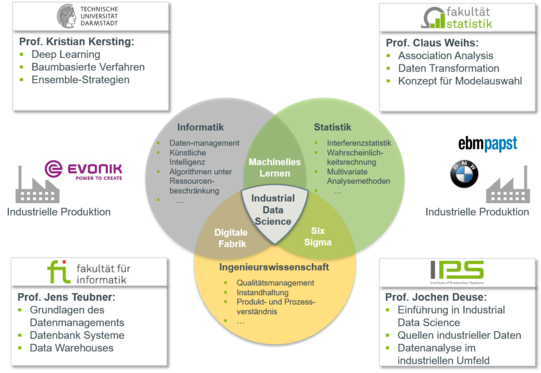
The teaching concept should integrate two essential and innovative features. On the one hand, a practice-oriented transfer of knowledge in the field of machine learning to solve real problems in manufacturing companies and, on the other hand, learning in heterogeneous groups of students of statistics, computer science and engineering as well as specialists from industry. The concept will thus meet the demand for the highest possible practical relevance and promote an intensive, interdisciplinary exchange. In order to realise the planned research goals, a two-part training programme is to be developed, which will first focus on teaching the theoretical content of machine learning and data management and then evaluate the application of these using practical application scenarios from industry as examples.
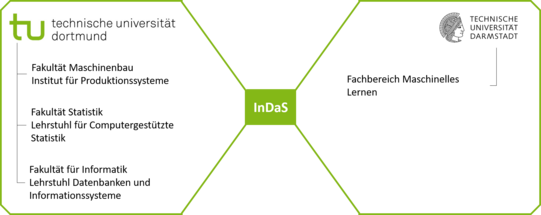
Research- and Development Partner
- Chair of Computational Statistics, TU Dortmund
- Chair VI Databases and Information Systems, TU Dortmund
- Institute of Production Systems, TU Dortmund
- Department of Machine Learning, TU Darmstadt
Förderhinweis
This research and development project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research as part of the programme "ICT 2020 - Research for Innovation" and is supervised by the German Aerospace Centre.

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/storages/zentraler_bilderpool/_processed_/2/6/csm_Altes_Maschinenbau-Gebaeude_3a1a87015a.jpg)